Proxy
Author Ter-Petrosyan Hakob
The Proxy design pattern is a structural pattern. It is one of the simplest patterns to understand and use.
The Gang of Four defines the proxy pattern as:
Provide a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it.
In other words, a proxy acts as a gatekeeper. It sits between a client and a real object. The proxy can:
- Check permissions before operations
- Log or monitor requests
- Limit or modify access
- Cache results or delay object creation
This helps you protect sensitive actions or manage resource use without changing the real object or the client code.
Class Diagram:
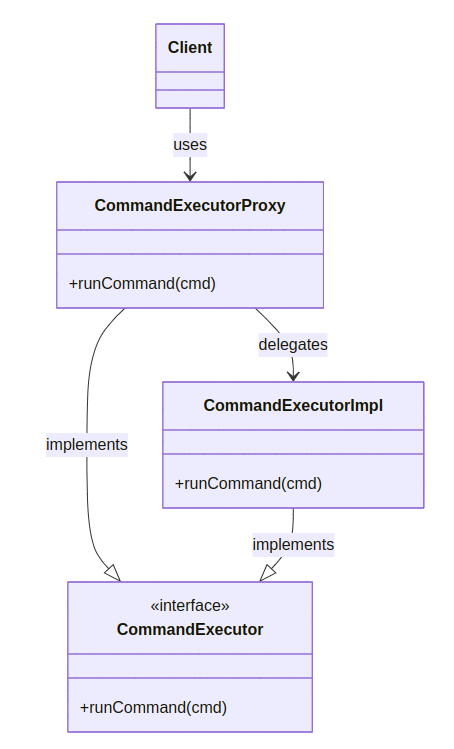
This class diagram illustrates the structure of the Proxy pattern:
CommandExecutoris an interface definingrunCommand(cmd).CommandExecutorImplis the real object that implementsCommandExecutor.CommandExecutorProxyalso implementsCommandExecutorand controls access before delegating to the real implementation.- The Client uses the proxy rather than the real object directly, ensuring safe access.
Example: Command Executor
Imagine a class that runs system commands. If you give it directly to a client, they could run dangerous commands like rm -rf /.
We can use a proxy to prevent that.
CommandExecutor Interface:
public interface CommandExecutor {
void runCommand(String cmd) throws Exception;
}
Real Command Executor:
public class CommandExecutorImpl implements CommandExecutor {
@Override
public void runCommand(String cmd) throws UnauthorizedException, CommandExecutionException {
// Execute the system command
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
System.out.println("Executed: '" + cmd + "'");
}
}
Proxy Class:
public class CommandExecutorProxy implements CommandExecutor {
private static final String ADMIN_USER = "Gurgen";
private static final String ADMIN_PWD = "J@urnalD$v";
private final CommandExecutor executor;
private final boolean isAdmin;
public CommandExecutorProxy(String user, String pwd) {
Objects.requireNonNull(user, "user cannot be null");
Objects.requireNonNull(pwd, "pwd cannot be null");
this.executor = new CommandExecutorImpl();
this.isAdmin = ADMIN_USER.equals(user) && ADMIN_PWD.equals(pwd);
}
@Override
public void runCommand(String cmd) throws UnauthorizedException, CommandExecutionException {
Objects.requireNonNull(cmd, "cmd cannot be null");
String trimmed = cmd.trim();
if (!isAdmin && trimmed.startsWith("rm")) {
throw new UnauthorizedException("Permission denied: non‑admin users cannot execute 'rm' commands.");
}
try {
executor.runCommand(cmd);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CommandExecutionException("Error executing command: " + trimmed, e);
}
}
}
Client Code:
public class ProxyPatternTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CommandExecutor executor = new CommandExecutorProxy("Gurgen", "wrong_pwd");
try {
executor.runCommand("ls -ltr");
executor.runCommand("rm -rf abc.pdf");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
In this example:
- The client uses
CommandExecutorProxyinstead ofCommandExecutorImpl. - The proxy allows safe commands for all users.
- It blocks dangerous commands for non-admin users.
Sequence Diagram
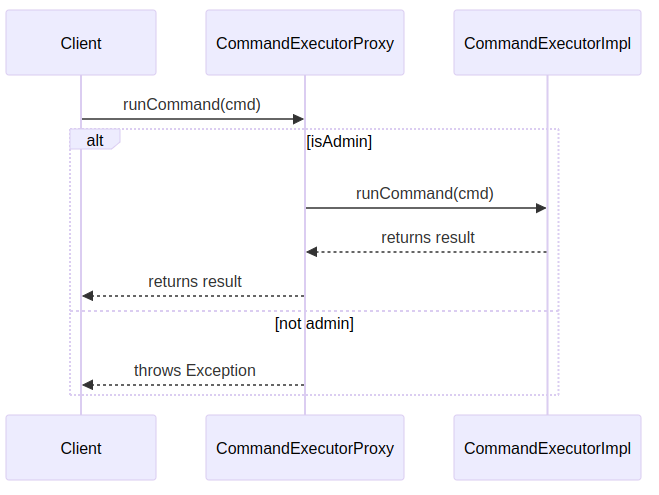
This sequence diagram shows how the Proxy handles a client request:
- The Client calls
runCommand(cmd)on theCommandExecutorProxy. - The Proxy checks if the user is an admin:
- If
admin, it delegates the call toCommandExecutorImpland returns the result. - If not
admin, it throws an exception for disallowed commands.
- If
Common Uses of Proxy Pattern
- Virtual Proxy (Lazy Initialization): Delay creating a heavy object until it is really needed.
- Protection Proxy (Access Control): Allow only certain clients to use the object.
- Remote Proxy (Remote Service): Handle network communication to a remote object.
- Logging Proxy: Log each request before passing it to the real object.
- Caching Proxy: Cache results of expensive operations and reuse them.
- Smart Reference: Track and manage the lifecycle of a service object, freeing resources when no one uses it.
Pros&Cons
Pros:
- Control access without changing the original object.
- Add features (logging, caching, security) transparently.
- Delay object creation and save resources.
- Follow the Open/Closed Principle: you can add new proxies without changing existing code.
Cons:
- More classes to manage, which can lead to complexity.
- Extra layer may add some performance overhead.
Relation to Other Patterns
- Adapter provides a different interface to an object. Proxy uses the same interface.
- Decorator adds responsibilities to an object. Proxy controls or manages access to the object.
- Facade simplifies access to a group of objects. Proxy controls access to a single object.