The Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean theorem is one of the most famous results in mathematics. It describes a special relationship between the sides of a right triangle - a triangle that has one angle of exactly \(90\) degrees (a right angle).
The theorem says:
\[a^2 + b^2 = c^2\]Where:
- \(a\) and \(b\) are the legs (the shorter sides meeting at the right angle).
- \(c\) is the hypotenuse (the longest side, opposite the right angle).
In words: The square built on the hypotenuse is equal in area to the sum of the squares built on the other two sides.
A rectangle can help us see the theorem in action. If we draw a diagonal in a rectangle, it divides the rectangle into two right triangles.
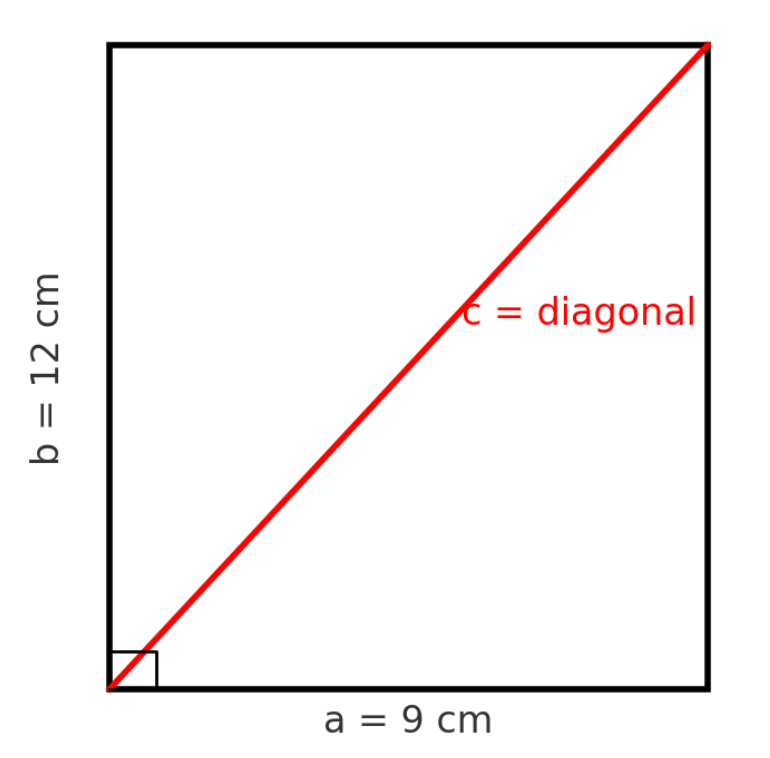
A rectangle is \(9\) cm wide and \(12\) cm tall. Find its diagonal:
\[c = \sqrt{9^2 + 12^2} = \sqrt{81 + 144} = \sqrt{225} = 15\]This is used in real life for:
- Measuring TV and monitor sizes
- Construction work
- Finding distances on maps